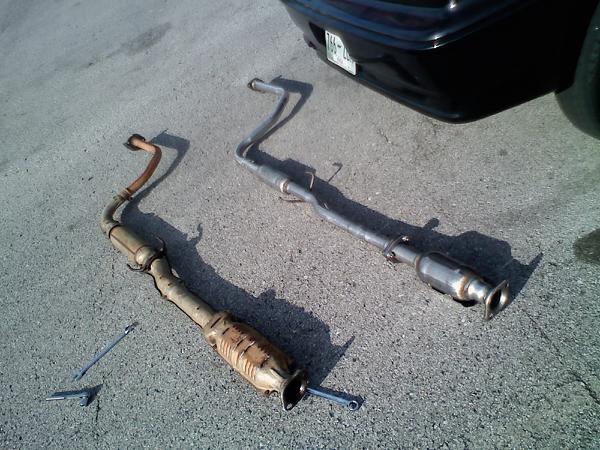
- How a Catalytic Converter Controls Pollution
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- What Materials are Used in the Construction
- Role of Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium
- Chemistry Behind a Converter’s Functionality
- Diagnose Problems with a Catalytic Converter
- Installing an Aftermarket Catalytic Converter
- Environmental Benefits of a Catalytic Converter
- Signs Your Car Needs a New Catalytic Converter
- Maintaining Your Car’s Existing Converter
How a Catalytic Converter Works to Reduce Pollution
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system that helps reduce the number of pollutants released into the atmosphere. It works by converting harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, into less harmful substances before they are released from the tailpipe. This process is known as catalytic oxidation. So, what’s inside a catalytic converter?
The catalytic converter consists of a ceramic or metal honeycomb structure coated with a catalyst material, usually platinum, palladium, or rhodium. When exhaust gases pass through this honeycomb structure, they come in contact with the catalyst material which causes chemical reactions to take place.
You can learn more about these precious metals in our explainers on how much platinum is in a catalytic converter, as well as which catalytic converters have the most rhodium. These reactions convert carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water vapor which are much less harmful to the environment than their original forms.
The efficiency of a catalytic converter depends on its design and how well it is maintained over time. If it becomes clogged or damaged due to age or lack of maintenance, its effectiveness will be reduced significantly, and more pollutants will be released into the atmosphere than if it were functioning properly.
Catalytic converters have been mandatory on all new vehicles since 1975 to reduce air pollution caused by vehicle emissions. You can learn more about what’s inside them and how they work in our guides on what is a catalytic converter made of, as well as whether do you need a catalytic converter.
They have been highly effective in reducing emissions from cars and trucks but their effectiveness can be further improved if drivers ensure that their vehicles are regularly serviced according to manufacturer recommendations so that any potential problems can be identified early on before they become serious issues that could lead to increased emissions levels.
The Different Types of Catalytic Converters and Their Benefits
Catalytic converters are an essential part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. They are designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. There are several different types of catalytic converters available, each with its own unique benefits (and differentiating what’s inside a catalytic converter).
- The most common type is the three-way catalytic converter, which is used in gasoline-powered vehicles. This type of converter uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). The three-way catalytic converter also reduces nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx), making it one of the most effective pollution control devices available for gasoline engines.
- Another type is the diesel oxidation catalyst, which is used in diesel engines. This device works by oxidizing unburned hydrocarbons and reducing particulate matter from diesel exhaust gases. It also helps reduce NOx emissions from diesel engines as well as other pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2).
- The last type is the selective catalytic reduction system, or SCR system for short. This device uses urea or ammonia to reduce NOx emissions from both gasoline and diesel engines by up to 90%. It can also help improve fuel economy by up to 5%.
Each type of catalytic converter has its own unique benefits that make it suitable for different applications depending on your needs. All types offer improved air quality while helping you save money on fuel costs at the same time. This should also help with explaining what’s inside a catalytic converter.
What Materials are Used in the Construction of a Catalytic Converter?
Catalytic converters are an important component of modern vehicle exhaust systems. They are designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances.
The materials used in the construction of a catalytic converter include a ceramic or metal honeycomb substrate, precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, and other materials such as aluminum oxide and silicon carbide.
The ceramic or metal honeycomb substrate is typically made from cordierite or stainless steel. This substrate provides a large surface area for the catalysts to adhere to and helps ensure that exhaust gases flow evenly through the converter.
Precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium act as catalysts that help convert pollutants into less harmful substances. These metals are usually applied in very thin layers onto the substrate using a process called thermal spraying.
Aluminum oxide is often used in combination with precious metals to increase its effectiveness at reducing emissions. Silicon carbide is also sometimes added to increase durability and reduce heat transfer from hot exhaust gases passing through the converter.
Finally, some converters may also contain additional components such as oxygen sensors or particulate filters for further emission reduction capabilities. Also, if you’re scrapping your car for its metals, check out our guide on the catalytic converter precious metal scrap prices.
The Role of Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium in Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are an essential component of modern automobiles, as they help reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. These devices rely on a combination of precious metals, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium (among those of what’s inside a catalytic converter), to convert toxic gases into less harmful substances.
Platinum is the most commonly used metal in catalytic converters due to its ability to efficiently oxidize carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. It also helps reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by converting them into nitrogen and oxygen molecules.
Palladium is another important metal used in catalytic converters because it can effectively reduce carbon monoxide levels while also helping to control hydrocarbon emissions. Finally, rhodium is used in some catalytic converters because it has a higher oxidation potential than either platinum or palladium and can therefore help further reduce emissions levels.
The three metals work together to create a chemical reaction that breaks down pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. Platinum acts as an oxidizing agent that converts carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide molecules; palladium helps break down nitrogen oxide molecules; while rhodium further reduces emission levels by increasing oxidation potentials within the converter itself.
In summary, platinum, palladium, and rhodium play an important role in catalytic converters by helping convert toxic gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the environment. The combination of these three metals allows for efficient conversion rates that help protect our air quality from dangerous pollutants emitted from automobiles.
Understanding the Chemistry Behind a Catalytic Converter’s Functionality
A catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. It works by converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
To understand how this process works, it is important to first understand the chemistry behind it.
- The catalytic converter contains a ceramic honeycomb structure coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
- When exhaust gases pass through this honeycomb structure, they come into contact with these metal surfaces which causes them to react with oxygen molecules in the air. This reaction produces harmless compounds like carbon dioxide and water vapor instead of more hazardous ones like nitrogen oxides or unburned hydrocarbons.
- The catalyst also helps reduce emissions by increasing the temperature at which combustion takes place inside an engine’s cylinders. This higher temperature causes more complete combustion of fuel molecules which results in fewer pollutants being released from the tailpipe.
In summary, a catalytic converter uses precious metal-coated ceramic honeycomb structures (which is what’s inside a catalytic converter) to convert toxic exhaust gases into less harmful compounds while also raising combustion temperatures for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions from vehicles’ tailpipes.
How to Diagnose Problems with Your Car’s Catalytic Converter
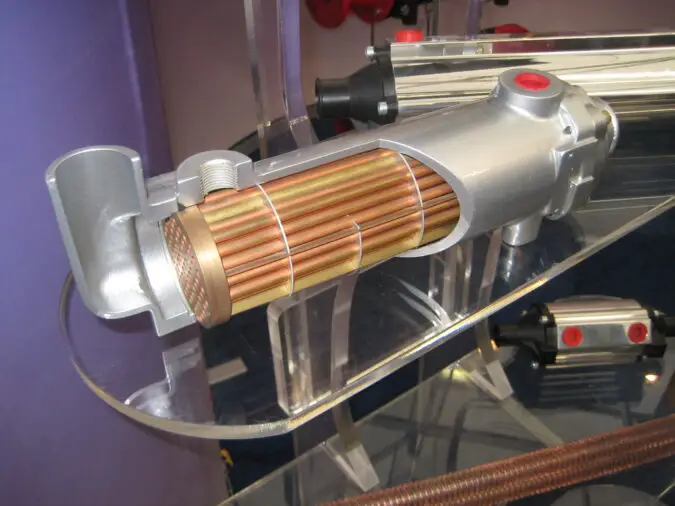
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
The catalytic converter is an important part of a car’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. If your car’s catalytic converter is not functioning properly, it can cause a variety of problems with your vehicle. To diagnose and repair any issues with your car’s catalytic converter, you will need to follow these steps:
1. Check for engine misfires or rough idling. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can cause engine misfires or rough idling due to an accumulation of unburned fuel in the exhaust system. If you notice either of these symptoms, it could be a sign that there is something wrong with your car’s catalytic converter. For more insight, check out our guide on whether can a bad catalytic converter cause a misfire.
2. Inspect the oxygen sensor readings on your vehicle’s computer system. The oxygen sensor monitors how much oxygen is present in the exhaust gases and sends this information back to the computer system for it to adjust fuel delivery accordingly. If there are any discrepancies between what should be normal readings and what is being read by the computer, then this could indicate that there may be an issue with your car’s catalytic converter.
3. Look for signs of physical damage to the catalytic converter on the outside of the unit itself such as cracks or holes in its casing or discoloration from heat damage caused by excessive temperatures inside its chamber due to clogged passages within its honeycomb structure which can lead to reduced efficiency and performance levels from its intended purpose as well as increased emissions output from unburned fuel passing through without being converted into harmless gasses like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
4. Have a professional mechanic inspect and test your vehicle’s exhaust system using specialized diagnostic equipment such as an OBD-II scanner which can detect any faults within various components including those related directly or indirectly related to a faulty catalytic converter like air/fuel ratio sensors, mass airflow sensors, etc., so they can accurately pinpoint exactly where any issues lie before attempting repairs or replacements if necessary.
5. Replace any faulty parts identified during testing if needed; this may include replacing just one component such as an oxygen sensor rather than having to replace entire sections like mufflers/exhaust pipes etc., depending on what has been found during inspection/testing procedures carried out by qualified technicians who have experience working on vehicles equipped with modern emission control systems including those containing cat converters.
The Pros and Cons of Installing an Aftermarket Catalytic Converter
Installing an aftermarket catalytic converter is a popular choice for many car owners, as it can help reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency (all thanks to what’s inside a catalytic converter). However, there are both pros and cons to consider before making the decision to install one.
The Pros:
1. Improved Fuel Efficiency: Aftermarket catalytic converters are designed to be more efficient than factory-installed models, which can result in improved fuel economy. This means that you may be able to save money on gas over time.
2. Reduced Emissions: Aftermarket catalytic converters are designed to reduce harmful emissions from your vehicle, which can help protect the environment and improve air quality in your area.
3. Increased Performance: Installing an aftermarket catalytic converter can also increase engine performance by reducing backpressure in the exhaust system, resulting in improved acceleration and power output from your vehicle’s engine.
The Cons:
1. Costly Installation Process: Installing an aftermarket catalytic converter is not a cheap process; it requires specialized tools and knowledge of how the system works, so you may need to hire a professional mechanic or technician for installation services if you don’t have these skills yourself or access to the necessary tools at home.
2. Potential Legal Issues: Depending on where you live, installing an aftermarket catalytic converter may be illegal due to stricter emission standards set by local governments. Be sure to check with your local laws before making any modifications that could potentially put you at risk of fines or other legal issues.
3. Reduced Durability: While aftermarket converters are designed for increased efficiency, they often lack durability compared with factory-installed models, meaning they may need replacing sooner than expected.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. By converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances (catalyzed by what’s inside a catalytic converter), catalytic converters play a vital role in reducing air pollution.
The environmental benefits of using a catalytic converter are numerous. Firstly, they help to reduce emissions of carbon monoxide (CO), which is a major contributor to global warming and climate change.
Catalytic converters also reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), which can cause smog and acid rain when released in large quantities. Additionally, they help to minimize the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can contribute to ground-level ozone formation and respiratory problems in humans.
In addition to these direct environmental benefits, using a catalytic converter can also improve fuel efficiency by reducing engine drag caused by unburned fuel particles entering the exhaust system. This helps vehicles run more efficiently while consuming less fuel, resulting in fewer greenhouse gas emissions overall.
Overall, it is clear that using a catalytic converter has many positive environmental impacts due to its ability to reduce air pollution from vehicle exhaust systems. By helping minimize emissions of CO2 and other pollutants that contribute to global warming and climate change, catalytic converters play an important role in protecting our environment for future generations.
Common Signs That Your Car Needs a New or Replaced Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances.
Unfortunately, over time, this part can become damaged or worn out and require replacement (including what’s inside a catalytic converter). Here are some common signs that your car may need a new or replaced catalytic converter:
1. Check Engine Light: One of the most common signs that your car needs a new catalytic converter is if the check engine light comes on and stays on. This could indicate that there is an issue with the emissions system, which could be caused by a faulty catalytic converter.
2. Poor Fuel Economy: If you notice that your fuel economy has decreased significantly, it could be due to an inefficiently functioning catalytic converter. A clogged or damaged part can cause your engine to work harder than normal to produce power, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions output.
3. Excessive Exhaust Smoke: If you notice excessive smoke coming from your exhaust pipe, it could be due to a faulty catalytic converter not properly converting pollutants into harmless gases before they are released into the atmosphere. This smoke will usually have a strong odor as well as be visible when looking at the tailpipe of your vehicle while running it at idle speed for several minutes or more.
4. Rattling Noises: Another sign that you may need to replace your car’s catalytic converter is if you hear rattling noises coming from underneath the vehicle when accelerating or decelerating. This noise indicates that something inside of the exhaust system has come loose and needs attention immediately.
Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s Existing or Replacement Catalyst Converters
1. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle. This includes regular oil changes, tune-ups, and other services that will help keep your car running smoothly and efficiently.
2. Make sure to use the correct fuel grade for your vehicle as specified by the manufacturer. Using a lower grade of fuel can cause damage to the catalytic converter over time.
3. Avoid idling for long periods as this can cause excessive heat buildup in the catalytic converter which can lead to premature failure or damage to its components.
4. If you notice any signs of trouble with your catalytic converters such as a decrease in performance or an increase in exhaust emissions, have it checked out immediately by a qualified mechanic or technician who specializes in exhaust systems and emission control devices such as catalytic converters.
5. If you are replacing an existing catalyst converter, make sure that it is compatible with your vehicle’s engine type and size before installation so that it functions properly and efficiently without causing any additional problems down the road due to incompatibility issues between parts or components within the system itself.
6. Make sure that all connections are secure when installing a new catalyst converter so that there is no risk of leaks or other issues which could potentially damage both the new part and other components within your car’s exhaust system.
7. Check regularly for any signs of wear on both existing and replacement parts so that they remain functioning properly at all times (not to mention, what’s inside a catalytic converter).

